Terminology 3D-orientation |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
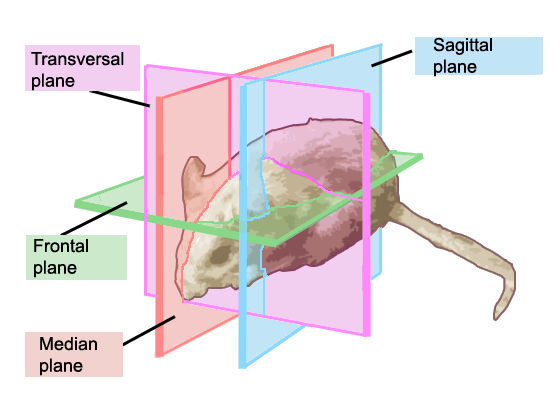
Orientation terminology for the study of 2-D and 3-D structures in biologyOrientation terms, derived from Greek or Latin, are used to define the position of certain structures with respect to others in organisms and to certain anatomical surfaces in sections. Frequently used terms are regrouped in the tables here below (main source: manuals written by Dr. François van Herp) 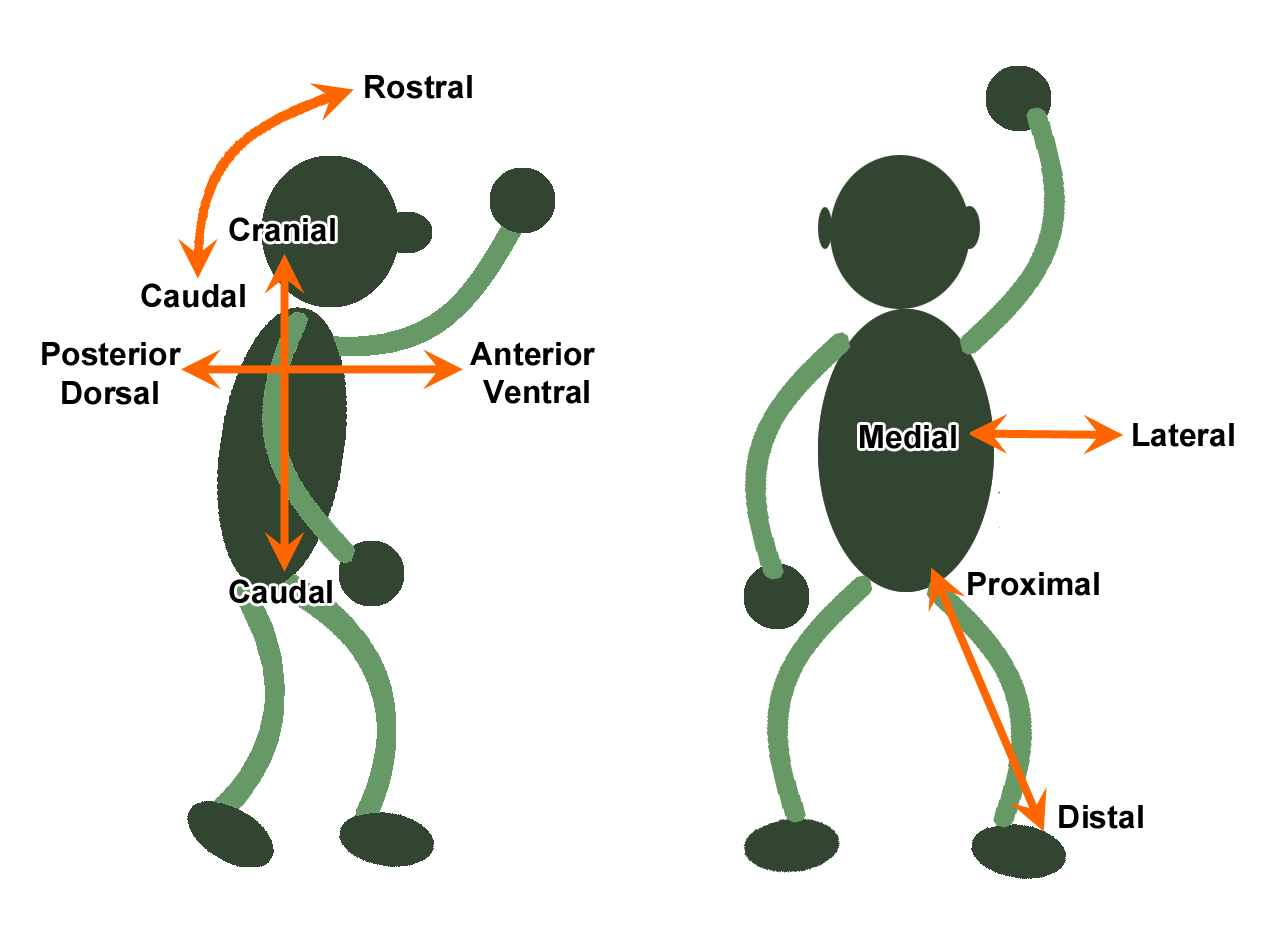
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||