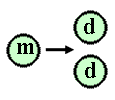
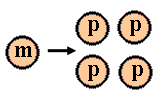
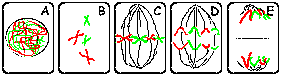
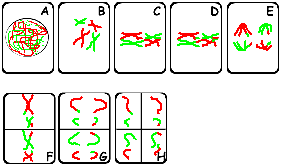
Mitosis vs meiosis |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
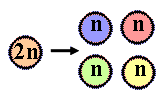
Differences between mitosis and meiosisView animations and movies on -the differences between- mitosis and meiosis.
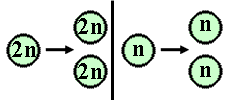
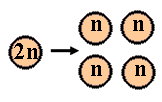
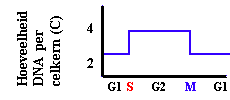
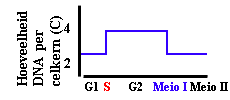
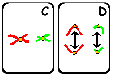
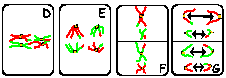
The mitotic metaphase can be distinguished from the metaphase I of meiosis as no pairing of homolog chromosomes occurs in mitosis; this is not necessary, even not suitable for the mitotic process (why?). Further, homolog chromosomes separate during metaphase I of meiosis, whereas during mitosis and metaphase II the separating structures are the chromatides. The difference between the separation in mitosis and metaphase II (meiosis) is that halfing of the number of chromosomes has preceeded meiosis II, in contrast to mitosis. Also the meiotic products are genetically diverse with respect to their parent and among each other. This is not the case in mitosis! |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||