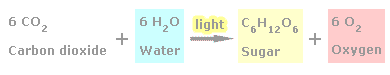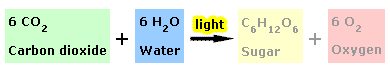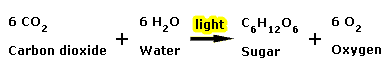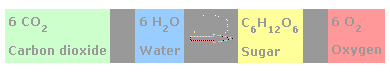Photosynthesis |
||
Plants occupy a fundamental position in the food web, since they serve as the primary source (producers) of organic compounds for animals and humans. Plants utilize their leaves to produce sugars in a process that involves light and which is called photosynthesis. Simplified (Fig. 1), water (H2O, the source of H and O) and carbon dioxide (CO2, the source of C) are transformed into sucrose (a sugar = C6H12O6) and oxygen (= O2 to the atmosphere) in a process in which light energy is consumed:
Movie 'Plants: photosynthesis' of Britannica.com | ||