Leaves of dicotyledonous plants show a great variation in shape (see some examples in the drawing below). The venation show a hand-shaped or feather-like pattern, while stomata are randomly spread over the leaf surface, as well as the epidermal cells with the shape of "puzzle-pieces". See zoomable examples of these features in
ivy,
petunia and
lilac. How leaves are formed in dicots is explained
elsewhere.
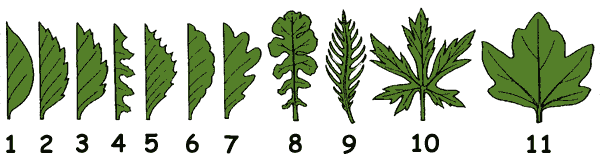
| Leaf margin in dicots |
|
|
1. Smooth (entire). 2. Serrate. 3. Double serrate. 4.Saw-shaped. 5. Toothed. 6.Crenate. 7. Lobed. 8. Parted. 9. Pinnately (like a feather) incised. 10. Palmately (like a hand) incised. 11.Palmately (like a hand) lobbed.
|
| Ivy |
 |
 |
 |
| Upper side leaf |
Close-up showing venation |
Stomata on an ivy leaf section |
| Petunia: Morphology and epidermal strips |
 |
 |
 |
| Young petunia plant |
Upper side leaf |
Lower side leaf |
 |
 |
 |
| Close-up of a petunia leaf |
Epidermis of a petunia leaf |
Epidermis strip of a petunia leaf |
| Lilac: Morphology (upper views) and sections (lower views) |
 |
 |
 |
| Lilac branch |
Upper side leaf |
Lower side leaf |
 |
 |
 |
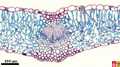
| Cross-section, overview |
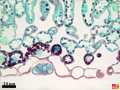
Detail of a cross-section of a lilac leaf |
Section through the leaf surface with stoma and trichome |